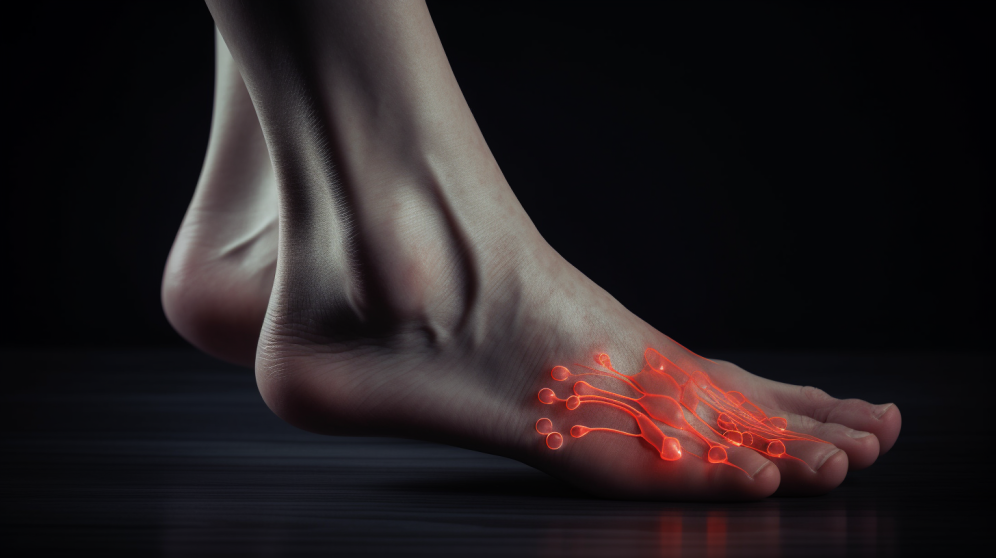
Morton’s Neuroma is a frequently encountered foot condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Morton’s Neuroma, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. By understanding the nature of this condition, you can take proactive steps to address the discomfort and pain associated with it.
What is Morton’s Neuroma?
Morton’s Neuroma, also known as interdigital neuroma, is a nerve condition that primarily affects the forefoot, most commonly between the third and fourth toes. It involves the thickening or enlargement of the nerve tissue, typically in response to repetitive stress or irritation. This results in the compression and irritation of the affected nerve, leading to pain and discomfort.
Causes of Morton’s Neuroma
The precise cause of Morton’s Neuroma is not fully understood. However, several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These include:
- Footwear: Wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, particularly those with high heels or narrow toe boxes, can increase the risk of Morton’s Neuroma. Such footwear places excessive pressure on the toes and forefoot, leading to nerve irritation.
- Foot Biomechanics: Certain foot deformities or abnormalities, such as bunions, hammertoes, or flat feet, can alter the distribution of weight and increase pressure on the nerves, making individuals more susceptible to developing Morton’s Neuroma.
- Repetitive Stress: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive stress on the forefoot, such as running, jumping, or participating in sports, can contribute to the development of Morton’s Neuroma over time.
- Footwear with Minimal Support: Wearing shoes that lack adequate arch support or cushioning can increase the strain on the forefoot, potentially leading to the formation of a neuroma.
Symptoms of Morton’s Neuroma
The symptoms of Morton’s Neuroma can vary in severity from mild discomfort to intense pain. Individuals with this condition commonly experience:
- Pain and Discomfort: Persistent pain or a burning sensation in the forefoot, often localized between the affected toes. The pain may worsen with walking, running, or wearing tight shoes.
- Numbness and Tingling: Some individuals may experience a tingling sensation or numbness in the affected area, extending to the toes. This can cause a loss of sensation or a feeling of pins and needles.
- Feeling of a Lump or Pea under the Foot: Morton’s Neuroma can create a sensation of having a small lump or an object, such as a pebble, under the ball of the foot.
- Worsening Symptoms over Time: If left untreated, the symptoms of Morton’s Neuroma may progressively worsen, leading to increased pain and difficulty in performing everyday activities.
Diagnosis of Morton’s Neuroma
When individuals experience symptoms indicative of Morton’s Neuroma, it is crucial to seek professional medical evaluation. A healthcare provider, typically a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist, will perform a comprehensive assessment, including:
- Medical History: The healthcare provider will inquire about the individual’s symptoms, their duration, and any potential triggers or exacerbating factors.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination will be conducted, focusing on the affected foot. The healthcare provider may palpate the area to elicit pain and assess the range of motion.
- Diagnostic Imaging: In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to rule out other conditions and visualize the neuroma.
Treatment Options for Morton’s Neuroma
The treatment approach for Morton’s Neuroma aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent further nerve irritation. The specific treatment options may vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual factors. Common treatment modalities include:
- Footwear Modifications: Wearing shoes with a wide toe box and low heels can help relieve pressure on the affected area and reduce symptoms. Avoiding high heels and tight-fitting footwear is crucial to minimizing nerve compression.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom orthotic inserts or arch supports can provide cushioning and support to the foot, redistributing pressure and relieving discomfort.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation associated with Morton’s Neuroma. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to alleviate symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Certain stretching and strengthening exercises can be recommended by a physical therapist to improve foot biomechanics and reduce nerve compression. Additionally, techniques such as ultrasound therapy or electrical stimulation may be employed to promote healing.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be considered. The surgical procedure aims to remove the affected nerve tissue or release pressure on the nerve, thereby alleviating symptoms.
Prevention and Self-Care Tips
While Morton’s Neuroma may not always be preventable, adopting certain preventive measures can reduce the risk of its development or progression. Consider the following self-care tips:
- Choose Proper Footwear: Opt for shoes that provide ample toe space, sufficient arch support, and cushioning. Avoid high heels and narrow-toed shoes that can contribute to nerve compression.
- Maintain Healthy Foot Biomechanics: Strengthening foot muscles and maintaining good posture can promote proper weight distribution and reduce the strain on the forefoot.
- Take Regular Breaks: If your occupation or activities involve prolonged standing or walking, take regular breaks to relieve pressure on the feet and avoid overloading the forefoot.
- Manage Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate pressure on the feet and reduce the risk of developing foot conditions such as Morton’s Neuroma.
- Listen to Your Feet: Pay attention to any foot discomfort or pain and seek prompt medical evaluation if symptoms persist or worsen.
Conclusion
Morton’s Neuroma is a common foot condition characterized by pain, discomfort, and nerve compression in the forefoot. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment can greatly improve one’s quality of life. By implementing preventive measures and adopting suitable treatment modalities, individuals can effectively manage Morton’s Neuroma and minimize its impact on daily activities. If you suspect you may have Morton’s Neuroma, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.